Advances in the Extraction and Emulsification System of Oil Bodies: A Review
-
摘要: 油体是植物组织中贮存油脂的特殊细胞器,三酰甘油构成了油体的疏水性内核,磷脂分子和油质蛋白构成油体外层的单层膜结构,赋予油体良好的稳定性,能够抵抗干旱、高温等外界不利条件,并能保持油体在体外水溶液中的稳定,具有广阔的开发前景。本文对植物油体的组成和结构、植物油体的提取及油体乳液乳化体系(如油体乳液乳化体系组成、乳化体系的稳定性及其乳化机理)等的研究进展进行综述,以期为水(酶)法提取植物油过程中乳液的有效破乳和植物油体产品的开发、应用提供参考。Abstract: The oil body is a special organelle for storing oil in plant tissues. Triglycerides form the hydrophobic core of the oil body, while phospholipid and oleosins form the monolayer membrane structure, giving the oil body good stability, which can resist drought, high temperature and other adverse external conditions and can keep the oil body stable in aqueous solution in vitro. In this paper, the composition and structure of vegetable oil body, the extraction methods and emulsification system of oil body including the composition, the stability of oil body emulsification system and its mechanism are reviewed, in order to provide reference for the technical improvement of effective demulsification during oil extraction by water (enzyme) method and the development and research of new oil-body products.
-
Keywords:
- oil bodies /
- extraction /
- emulsification system
-
植物油体(oil body)是植物种子、花粉等组织中贮存油脂的特殊细胞器,又称为油质体(oleosome)或脂质体(lipid body)。根据油体在植物组织中的分布,可分为两种—油质蛋白基脂质体(oleosin-based lipid body)和非油质蛋白基脂质体(non-oleosin-based lipid body)。植物种子中的脂质体主要是油质蛋白基脂质体(oleosin-based lipid body),占油料种子质量的40%~45%[1]。油体外层包裹着由磷脂单分子层和油质蛋白组成的磷脂-蛋白质单层膜,赋予油体良好的物理和化学稳定性,以抵抗干燥、高温等外界不利条件。
关于植物油体的研究主要集中在油体中脂肪的提取。比较成熟的植物油提取技术主要有物理压榨法和溶剂浸出法。物理压榨法包括热榨工艺和冷榨工艺,工艺简单,是最传统的制油方法。热榨工艺可以促进风味物质的形成,但是对热敏成分破坏大;冷榨工艺可以有效保护热敏成分,但出油率低,粕中残油量高[2-3]。溶剂浸出法的出油率高达95%以上,且生产成本低,但油品风味较差,存在有机残留,精炼工序繁琐,高温脱溶易造成湿粕中蛋白质等成分变性,不利于回收[4]。因此,近年来,水代法和在此基础上发展的水酶法由于绿色、环保、油品风味好、有效保留活性成分(如角鲨烯、生育酚[5]及多酚[6])等优点,成为研究的热点。但是水(酶)法制油工艺中,油料中的蛋白质、磷脂、糖及皂素等天然乳化成分吸附于油水界面发生乳化,降低了清油的得率,成为制约水(酶)法应用和推广的制约条件。本文对植物油体的组成和结构、油体提取技术和油体乳化体系的研究进展进行综述,以期为水(酶)法提油的有效破乳和油体产品的开发应用提供参考。
1. 植物油体的组成和结构
1.1 植物油体的组成
植物油体主要由中性脂(三酰甘油酯,tri-acylglycerol, TAG)、磷脂、蛋白质和其他微量组分组成,如钙离子、固醇类物质和辅酶等。三酰甘油酯构成油体的疏水性内核,而磷脂和镶嵌其中的油质蛋白,构成了油体外层的磷脂-蛋白质单层膜结构。因油料来源不同,中性脂约占油体质量的94.0%~98.0%,磷脂占0.6%~2.0%,而蛋白占0.6%~3.0 %[7-9](见表1)。蛋白质含量虽然较低,却是油体表面化学性质的主要贡献者。油质蛋白(oleosin)是油体膜蛋白中的主要组成部分,占油体膜蛋白含量的75%~80%。它是一个碱性小分子蛋白,分子量一般为14~17 kDa。除了油质蛋白,在油体膜中还存在着少量的油质钙蛋白(caleosin)和油质固醇蛋白(steroleosin),分子量分别为24~28 kDa和35~60 kDa[9]。由于提取和洗涤方法不同,油体表面还有可能残留部分外源蛋白。碱性pH提取[10]和连续多次洗涤[4]可以有效去除油体表面的外源蛋白,从而提高油体中TAG的相对含量。 磷脂中含量最高的是磷脂酰胆碱(PC),其次是磷脂酰丝氨酸(PS)、磷脂酰肌醇(PI)、磷脂酰乙醇胺(PE)等[8]。
油体来源 油菜籽 芥菜籽 棉籽 亚麻籽 玉米胚芽 花生 芝麻 车前草籽 脂质含量(%) 94.21 94.64 96.99 97.65 97.58 98.17 97.37 96.80 蛋白含量(%) 3.46 3.25 1.70 1.34 1.43 0.94 0.59 0.90 磷脂组成(%) 1.97 1.60 1.18 0.90 0.91 0.80 0.57 − 磷脂酰胆碱 59.50 53.10 58.60 57.20 64.10 61.60 41.20 55.10 磷脂酰丝氨酸 20.20 18.30 18.70 33.10 20.20 25.00 22.10 31.20 磷脂酰肌醇 14.00 13.10 18.10 6.90 7.60 8.40 20.90 11.70 磷脂酰乙醇胺 5.90 15.50 4.60 2.80 8.10 5.00 15.80 4.00 注:“−”表示文献中未列出。 1.2 植物油体的结构和形态
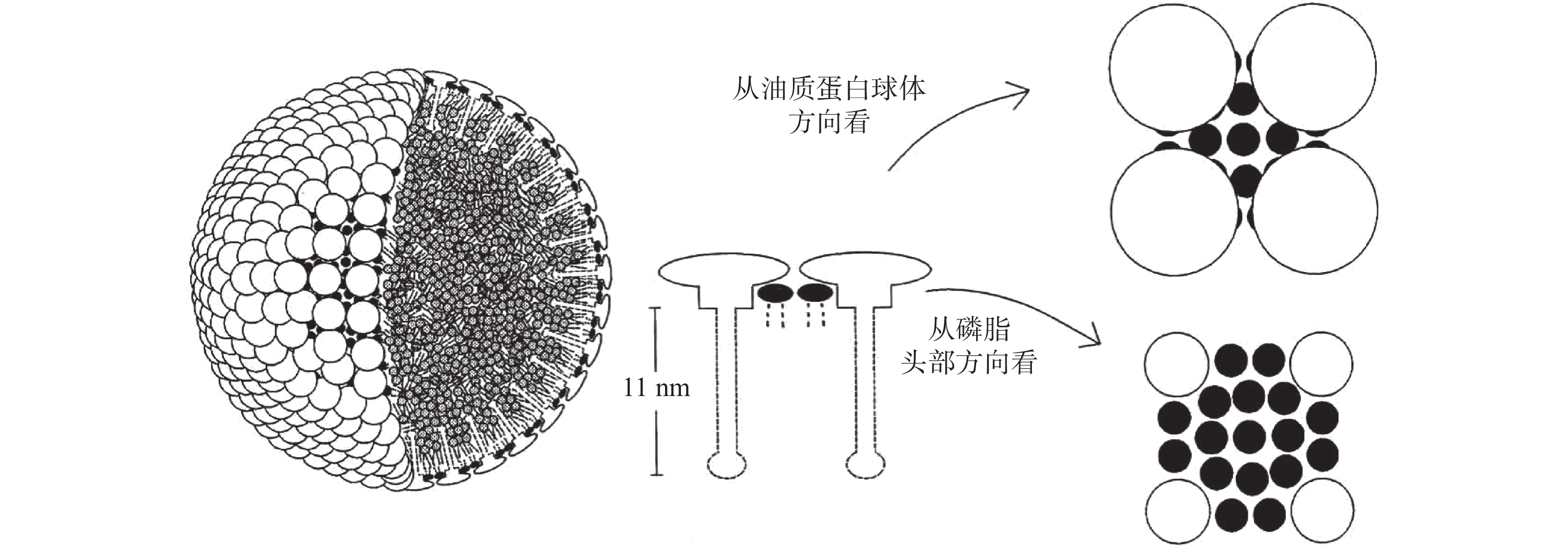
油料籽粒中的油体是种子进行新陈代谢的能量来源,占种子体积的75%以上[9]。目前,研究者普遍认可Tzen等[11]关于油体的三维结构模型(如图1),即三酰甘油酯(TAG)构成了油体的疏水性内核,其表面由磷脂单分子层和嵌在其中的油质蛋白构成。每个磷脂分子的疏水性尾部向内与疏水性的三酰甘油相互作用,而亲水性头部朝外定向于亲水环境。 油体单层膜结构的磷脂中饱和脂肪酸含量远远高于不饱和脂肪酸,延长的酰基为油质蛋白提供了足够的锚点[8]。油质蛋白由三个结构域组成:中心的疏水性结构域,由72个残基组成;N -末端的两亲性结构域,由50~70个残基组成;C-末端的两亲性结构域,长度可变,在靠近中心疏水性结构域方向的约33个残基可以形成两亲性α-螺旋结构,与带电磷酸盐和胆碱基团相互作用[12]。油质蛋白分子中疏水性的中心结构域形成一个11 nm的柄状结构,向内伸入三酰甘油内部和磷脂的疏水性酰基内部,具有两亲性的N-末端结构域和C-末端结构域向外覆盖于油体表面,提供空间位阻和静电斥力,来维持油体结构稳定[11]。C-末端的α- 螺旋结构还可能增加油质蛋白的疏水性,通过疏水相互作用增加油体结构的稳定性[13]。油质钙蛋白(caleosin)的结构与油质蛋白(oleosin)相似,也有三个结构域,不同的是在其N-末端亲水性结构域含有一个钙离子结合区,中心疏水性结构域含有一个高度保守的脯氨酸-结(pro-knot), C-末端含有蛋白激酶磷酸化位点,中心疏水结构域所占比例较小,而亲水性的N-末端和C-末端所占比例较大[14]。油质固醇蛋白(steroleosin)包括2个结构域:N-末端油体锚定区域和紧接其后的固醇结合脱氢酶区域,通过N-末端的疏水性片段将可溶性的固醇结合脱氢酶区域锚定在油体表面[15]。
![]() 图 1 植物油体的结构模型[11]注:油质蛋白分子相当于一个11 nm的柄状结构(中心疏水的发夹结构)附着在一个两亲性球状结构上(相当于未知二级结构的N-末端两亲性结构域和C-末端两亲性的α-螺旋结构域)。实线和圆表示亲水性组分,虚线表示疏水性组分。两线相连的黑色球体和三线相连的阴影球体分别代表磷脂和三酰甘油。(左)油体的尺寸与分子尺寸的比例被缩小了24倍;表面分子的曲率要比天然油体的曲率大得多(576倍);磷脂与油体的摩尔比保持与天然油体的摩尔比;油质蛋白与磷脂和油质蛋白的摩尔比显著降低。(中)垂直于表面的一个小的表面切片,显示两个油质蛋白分子和两个磷脂分子。(右)由13个磷脂分子和1个油质蛋白分子组成的结构单元的表面图。为了清晰地说明该结构单元,还展示了相邻的另外三个油质蛋白分子和四个磷脂分子。上面的图是在油质蛋白球体方向的视图,下面的图是在磷脂头部方向的视图。Figure 1. Structural model of oil bodies[11]
图 1 植物油体的结构模型[11]注:油质蛋白分子相当于一个11 nm的柄状结构(中心疏水的发夹结构)附着在一个两亲性球状结构上(相当于未知二级结构的N-末端两亲性结构域和C-末端两亲性的α-螺旋结构域)。实线和圆表示亲水性组分,虚线表示疏水性组分。两线相连的黑色球体和三线相连的阴影球体分别代表磷脂和三酰甘油。(左)油体的尺寸与分子尺寸的比例被缩小了24倍;表面分子的曲率要比天然油体的曲率大得多(576倍);磷脂与油体的摩尔比保持与天然油体的摩尔比;油质蛋白与磷脂和油质蛋白的摩尔比显著降低。(中)垂直于表面的一个小的表面切片,显示两个油质蛋白分子和两个磷脂分子。(右)由13个磷脂分子和1个油质蛋白分子组成的结构单元的表面图。为了清晰地说明该结构单元,还展示了相邻的另外三个油质蛋白分子和四个磷脂分子。上面的图是在油质蛋白球体方向的视图,下面的图是在磷脂头部方向的视图。Figure 1. Structural model of oil bodies[11]受外界环境影响,植物油体形状和大小各不相同。在高水分含量的葵花籽中,油体呈规则的球形,而在水分含量较低的玉米胚芽中,由于组织收缩,空间受限,油体呈不规则形状[16]。膜蛋白约占油体膜表面积的20%,其含量往往决定了油体粒径的大小。一般,油质蛋白与三酰甘油的比值越大,油体粒径越小。在水溶液中,由于相邻油体分子之间的空间位阻和静电斥力,油体形成粒径0.5~2.5 μm的球状微滴,不易聚集和融合,具有较好的稳定性[11]。有研究表明,油体表面除了磷脂和油质蛋白外,还可能有外源蛋白(extraneous protein)吸附于油体表面,形成第二层膜,增加了油体的稳定性[17-21]。
2. 植物油体的水法提取
由于油体表面具有亲水性,在水溶液中,油体可分散于水相形成均匀的乳液。利用这一特性,通常通过机械破碎(如磨浆)破坏植物细胞壁结构,并实现油体与蛋白体、淀粉粒的分离,同时,形成的细小颗粒,大大增加了油体与水的接触面积,有利于油体在水溶液中的分散;然后利用油体与蛋白质、淀粉、多糖等其他成分的溶解性和比重差异,借助离心实现油体的上浮,得到粗油体;采用碱溶液、蔗糖溶液、盐溶液及尿素等洗涤,去除油体表面粘附的其他杂质,提高油体纯度[7,11,22-26]。
根据油体的纯度和结构完整程度可将其分为纯油体、粗油体和修饰油体[7]。为了研究油体的结构、组成和性质,需要纯的油体。Tzen等[7,11]将冷水浸泡的种子(玉米胚芽、大豆、葵花籽、荷荷巴籽等)在0.6 mol/L蔗糖水溶液(内含EDTA、氯化镁、氯化钾、DTT,pH=7.5)中磨浆,过滤得到油体提取物,经蔗糖溶液连续离心浮选得到油体,采用0.1%吐温-20、2 mol/L氯化钠和9 mol/L尿素多次洗涤,得到高纯度的完整油体[22],提出了油体结构的经典模型,并对不同来源的油体结构和组成进行了分析。该方法在油体及油质蛋白的研究中被广泛采用[23-25]。Chen[26]将浸泡过的大豆在去离子水中磨浆,并采用含蔗糖的碱性溶液(pH=11.0)提取大豆油体,经多次碱洗和水洗去除外源性蛋白,研究了油质蛋白和磷脂在维持植物油体结构稳定中的关键作用。后来又提出了采用100 mmol/L Tris-HCl缓冲溶液(含3 mmol/L MgCl2, pH=8.6)作为浸提剂的两步提取法,使油体得率提高至65%,通过热处理钝化水解酶,以保持油体的长期稳定[27]。Zaaboul等[28]将花生经蒸馏水浸泡和研磨得到花生浆,并经过滤和蔗糖溶液离心浮选,得到粗油体,采用10 mmol/L磷酸缓冲溶液对油体进行回收,并分离出两种花生油质蛋白亚型(分子量分别为14 和16 kDa)。因此,提高油体纯度和完整度的关键是:a.控制研磨的程度,以保证油体结构的完整;b.控制提取条件(温度、盐离子强度、pH值等),从而促进油体的释放,抑制内源性水解酶的活力;c.控制洗涤条件(盐离子强度、pH、尿素等去污剂)及洗涤次数,以提高油体的纯度。
在油体结构研究中,为了得到高纯度油体,通常采用复杂的缓冲溶液(其中往往含有有机溶剂)和高速离心(离心力往往大于10000 g),工序繁琐,提取率低,存在有机残留风险。为了实现油体在食品、医药和化妆品行业的应用和推广,首先应考虑的是油体的得率和理化性质。Nikiforid等[17]对磨碎的玉米胚芽(粒径0.8 mm)进行三次连续碱提及两次低速离心(3800 g,30 min),制得玉米胚芽粗油体,油体得率高达95%,该油体可以长时间保持稳定而不絮凝。Kapchie等[29]提出了复合酶解(多功能果胶酶FE,纤维素酶A和多功能cx13l)结合三次0.05 mol/L Tris - HCl缓冲溶液(pH 7.2, 含0.5 mol/L NaCl,0.4 mol/L 蔗糖)连续提取,可以显著提高油体得率,所得油体中的油脂含量高达84.65%。Chirico[30-31]采用碳酸氢钠溶液(pH 9.5, 0.1 mol/L)对油菜籽进行浸泡、磨浆(固液比1:7),高速离心得到粗油体,然后采用碳酸氢钠溶液对粗油体进行洗涤,保证了油体结构的完整,而且油体纯度与9 mol/L 尿素洗涤所得油体纯度相同。因此,提高油体得率的关键是:a.油料的预处理(充分的机械破碎、高温、高压处理或适度酶解,充分破坏细胞壁);b.提取条件的控制(连续提取和离心的次数、pH、盐离子浓度等)。
3. 植物油体乳化体系研究
在油体提取的过程中,由于表面油质蛋白和磷脂的双亲性及油料组织中天然乳化成分(如:外源性蛋白、碳水化合物及皂素)的存在,油体提取物往往呈乳液状(emulsion)或奶油状(cream)。关于油体乳化体系的研究主要涉及提取、贮藏和加工过程中油体或油体乳液的稳定性及其乳化机理等方面。油体或油体乳液的稳定性主要与油体表面化学有关,油体的表面化学主要体现在油体表面电荷的多少、疏水相互作用的强弱及溶解性的好坏。而油体乳液的pH、盐离子强度、乳液浓度、乳化组分(如磷脂、油质蛋白、外源性蛋白、碳水化合物及皂素、外加表面活性剂等)、内源或外源水解酶、热处理等都会影响到油体的表面化学,从而改变油体之间相互作用力,最终影响油体乳液的稳定性。
3.1 维持油体及其乳液稳定的物质基础
油体的稳定性与其结构密切相关。油体表面的磷脂和蛋白质是具有两亲性的生物大分子,对于油体结构的稳定发挥着最基础的作用。磷脂包括甘油磷脂和鞘磷脂两类。植物中的磷脂主要以甘油磷脂为主。甘油磷脂分子中sn-1和sn-2位上的羟基与脂肪酸酯化,呈非极性;sn-3位的羟基与磷酸基团酯化,磷酸基进一步被高极性或带电荷的醇酯化,呈极性。因此磷脂具有一个极性头部和两个非极性尾部[32]。在O/W型乳状液中,磷脂和蛋白质形成复合物,用作乳化剂或乳化稳定剂[33]。阴离子磷脂的极性头部和油质蛋白之间发生强烈的静电相互作用,可以抵抗热变性;含长链饱和脂肪酸的阴离子磷脂与蛋白质之间的疏水相互作用有利于油质蛋白在油水界面形成更稳定的构象,为O/W型乳状液提供更好的物理化学稳定性[34]。植物油体中,磷脂的非极性尾部向内与三酰甘油结合,极性头部定向于胞质,形成磷脂聚合物,即磷脂单分子层,其结构特性不仅与磷脂的化学组成有关,而且受表面电荷分布、环境温度、盐离子强度等因素的影响[35]。
磷脂酰胆碱和磷脂酰丝氨酸是油体磷脂的主要成分[36]。由于磷脂酰胆碱可以与油体膜蛋白形成更强的疏水相互作用,因此,形成的油体乳液更稳定[37]。磷脂分子占到油体表面积的80%以上,构成油体表面膜结构的骨架[7]。油体表面膜蛋白虽然只占油体表面积的20%,但其疏水性中心结构域向内嵌于三酰甘油内部和磷脂的疏水性酰基内部,具有两亲性质的N-末端结构域和C-末端结构域向外伸展,带正电荷的残基与磷酸分子的负电荷相互作用,带负电荷的残基伸向油体表面,使油体表面整体带负电荷,彼此之间产生静电斥力。油质蛋白分子C-末端的α-螺旋结构使油体表面之间产生疏水相互作用和空间位阻,对维持油体的相对稳定发挥着主要作用[13]。油质蛋白的水解会使油体发生聚合,原因是油质蛋白的水解导致磷脂分子的暴露,此时油体表面化学发生改变,静电斥力和空间位阻减弱,导致油滴聚集[31]。由于油料来源[38]和提取方法[25]的差异,油质蛋白的含量、组成和分子量也不同,因此,表面电荷和疏水相互作用也存在差异,表现为油体粒径的大小不同,而油体粒径大小间接反映了油体乳液的稳定性。油体粒径越小,往往乳化液稳定性越好[39]。大豆纯油体的油质蛋白含量较高,油体粒径较小,因此,具有良好的稳定性。和大豆纯油体相比,采用同样提取和洗涤方法获得的花生、芝麻、油菜纯油体粒径相对较大,在等电点附近更易聚集,在中性pH条件下更易发生乳析现象[38]。
3.2 外源性蛋白对油体及其乳液稳定性的影响
油体表面油质蛋白分子和磷脂构成了油体表面的第一层膜结构,而外源性蛋白(主要是贮藏蛋白)构成了第二层膜,通过改变了油体表面的电荷特性,对油体的长期稳定发挥着举足轻重的作用[17-18,20]。一般认为,蛋白质稳定乳液的机理涉及到蛋白质向两相界面的迁移、分散及重排,使它的疏水分子朝向非极性相,而它的亲水分子朝向极性相;然后通过蛋白-蛋白分子聚合,形成具有粘弹性的界面膜,包裹在油滴上,并通过静电斥力和/或空间位阻来稳定乳液。蛋白质具有良好的乳化性,需要满足以下三个条件:高电荷性,使其能与界面结合,并在油滴被包裹后提供电荷斥力;良好的溶解性,使其更容易扩散到界面上,并在重排过程中表现出构象的灵活性;具有适度高疏水性,可形成具有一定强度的界面膜[39]。植物贮藏蛋白的等电点一般偏酸性,因此在中性至碱性溶液中一般带负电荷,在油体提取或贮藏过程中,贮藏蛋白会与油质蛋白之间形成蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用,在油体表面形成稳固的第二层膜,从而提高油体的稳定性。Yan等[40]发现大豆在浸泡和研磨过程中,外源性蛋白通过非共价键(大豆球蛋白和β-大豆伴球蛋白))和共价键(P34−24 kDa 油质蛋白和β-伴大豆球蛋白 (α’/α)−SS−P34−24 kDa 油质蛋白)与油体相连,其机理是:油体和外源性蛋白之间相互碰撞,将外源性蛋白的疏水链包裹进油体的三酰甘油基质,形成被外源蛋白修饰的油体;相邻油体之间的碰撞形成粒度不一的乳滴(其中可能嵌入了部分外源性蛋白)。当嵌入蛋白质的量达到临界值时,油体和油滴表面完全嵌入了油质蛋白、磷脂和外源性蛋白,将抑制外源性蛋白与油体乳滴的进一步结合。
3.3 内源性水解酶类对油体及其乳液稳定性的影响
在油体提取过程中,种子中的内源性蛋白酶会部分残留在油体中,导致油质蛋白的水解,破坏了油体表面的膜结构完整性,从而影响油体的贮藏稳定性。通常提取pH越低,油体表面的外源性蛋白含量越高,其中的水解酶活性越强。pH6.5弱酸性溶液提取的油体中除了油质蛋白外,还含有许多外源性蛋白(包括球蛋白、2S清蛋白和水解酶),该油体的油质蛋白被迅速水解,而且大分子油质蛋白比小分子油质蛋白更易被水解,说明pH=6.5弱酸性溶液提取的油体中水解蛋白酶活性较强;pH=8.0的碱溶液可以洗去球蛋白,pH=11的碱溶液可以去除包括2S清蛋白在内的外源性蛋白,得到高纯度油体(其中油质蛋白含量分别为豆薯79%,芝麻71%、花生81%、葵花籽91%),但是蓖麻籽油体中仍残留有15%的脂肪酶,菜籽油体中仍残留8%的水解酶(β-葡萄糖苷酶、过氧化物酶和乙醇脱氢酶) [40],说明外源性蛋白含量与水解酶活性之间并不存在绝对的对应关系。采用尿素和碱溶液(如pH9.5碳酸氢钠溶液)多次连续洗涤可以有效去除外源性蛋白,但酶活性仍然存在,导致油体在贮藏过程中出现聚集和分层。热处理是钝化酶活,提高乳状液稳定性的有效手段。短时间热处理(小于1 min)使得脂肪酶从油体表面向连续相中转移,导致连续相中酶活增加,可借助离心去除乳化层的大部分水解酶。长时间的热处理(大于1 min)可以使酶蛋白发生变性而失活,提高油体乳液的稳定性[31]。
3.4 pH和离子强度对油体及其乳液稳定性的影响
pH对油体及其乳液稳定性的影响主要由油体表面电荷分布决定。而油体表面电荷分布与油体表面蛋白质的电荷和构象密切相关。Qi等[41]对大豆油体表面蛋白的二级结构进行分析,发现大豆表面油质蛋白的疏水区域以α-螺旋结构为主,亲水区域由无规卷曲和β-折叠结构为主。在不同的酸碱(pH=2~11)溶液中, 油质蛋白的α-螺旋结构几乎没有变化,而碱性环境导致β-折叠结构增加,无规卷曲结构减少,说明高度保守的疏水核心是相当稳定的,而酸碱处理通过影响N-端和C-端亲水部分的二级结构,从而影响疏水区域的暴露程度,最终影响表面蛋白与电荷的结合能力以及表面净电荷的分布。
蛋白质是一种亲水胶体,在溶液中,蛋白质分子表面的亲水基团可与水分子形成水化层,因此,相互间不易靠拢而聚集。在低浓度的中性盐溶液中,蛋白质分子吸附盐离子,导致蛋白质与水的相互作用增强,溶解度增加;然而,大量中性盐的加入会降低水的活度,溶液中的自由水转化为盐离子的水化水,导致蛋白质水化层脱水,疏水性基团暴露,蛋白质分子之间的疏水相互作用增强,引起蛋白质聚集沉淀[42]。Hou 等[25]研究了氯化钠对三种油体(大豆、花生、葵花籽)热稳定性、表面疏水性和氧化稳定性的影响,当盐离子浓度为0 mmoL/L时,油体粒径最小。低盐离子浓度下,加入的离子通过静电屏蔽效应降低了油体表面电荷,改变了油体表面蛋白的结构,使表面疏水作用减弱,溶解性增加;随着盐离子浓度增加(从50 mmoL/L 升高至200 mmoL/L),油体电位降低,粒径增加,可能是高离子浓度减弱了油质蛋白N-和C-端与磷脂的相互作用,从而暴露出更多的疏水作用残基,导致油体之间疏水相互作用增强,从而出现聚集。由于蛋白质结构和氨基酸含量的不同,盐对不同种类油体粒径的影响不同,其中,大豆油体粒径最小,这可能是大豆油体中膜蛋白和三酰甘油比例最大,油体表面所带负电荷更高,彼此之间静电相互作用和空间位阻更大,因此稳定性更好。葵花籽油体乳化稳定性最好,可能是其中的蛋白质含量和疏水性氨基酸总量更高,增加了油体的界面膜厚度,提高了界面强度,从而增强了葵花籽油体的乳化能力。Juliana等[43]采用含一价阳离子(Na+、 K+) 或二价阳离子(Ca2+、 Mg2+) 的中性水溶液提取菜籽油体,发现含0.2 moL/L K+的中性溶液油体得率更高,与pH 9.5 碱溶液(含0.1 moL/L 碳酸氢钠)的得率相当,原因可能是阳离子与油体表面蛋白(也可能与磷脂分子)相互作用,改变了蛋白表面电荷特性及表面疏水性,从而影响其溶解性。因为Na+与磷脂分子的结合能力比K+更强[44],增加盐离子浓度,抵消了与磷脂分子结合的盐离子浓度,可以破坏蛋白质之间盐桥,提高膜蛋白与盐离子的结合,从而提高油体得率。但是,盐溶液提取的油体更容易聚集,油体粒径更大,可能是静电斥力减小,油体之间以及油体与被外源性蛋白修饰的油体之间疏水相互作用增强。二价阳离子与油质钙蛋白 N-端的钙离子结合位点结合,导致膜蛋白结构重排,抑制了膜蛋白之间的疏水相互作用,对油体的稳定不利[45]。
3.5 改善油体及其乳液稳定性的方法及其机理
为了改善油体在贮藏和加工中的稳定性,可以通过碱洗和(或)热处理降低或钝化内源水解酶的活性,或者外加乳化剂,如阴离子多糖或小分子表面活性剂,以抵抗极端pH和高离子强度对油体稳定性的不利影响。
阴离子多糖(如黄原胶、果胶、卡拉胶、海藻酸钠等)是天然的表面活性剂,通常用于O/W型乳液的稳定剂。多糖对乳化液的稳定受浓度影响。低浓度时,带负电荷的多糖可以与乳液中带相反电荷的蛋白质分子之间通过静电相互作用而吸附,形成弱的多层结构,增加液滴之间的静电斥力和空间位阻,降低了液滴之间的范德华力,从而提高乳化液稳定性;高浓度时,多糖往往通过黏度效应提高其乳化稳定性。添加0.1%的黄原胶可以显著提高低浓度玉米胚芽油体乳液的乳化稳定性,特别是对于富含外源性蛋白的油体乳液[18],可能是黄原胶分子与油体表面蛋白(特别是外源性蛋白)之间通过静电相互作用形成稳定的界面膜,降低了界面张力。低浓度的海藻酸钠与油体表面蛋白发生静电相互作用,提高油体在等电点附近的稳定性,从而延缓乳滴絮凝;高浓度的海藻酸钠通过增加乳化体系的粘度而延缓乳析现象的发生[38]。由于不同种类多糖表面电荷和结构的差异,稳定乳液的能力也不同[46]。Wu [47]分析了三种卡拉胶对不同pH大豆油体乳液的稳定效果,发现pH3~5时,卡拉胶和油体表面发生静电吸附,当卡拉胶添加量超过0.06 %时可以有效稳定乳化液。但是,λ-卡拉胶的加入使得液滴之间由于桥连而出现乳析现象。当pH7时,加入ι-卡拉胶的油体乳液更稳定,这可能要归功于ι-卡拉胶分子中的螺旋结构带有大量电荷,更易与油体表面发生相互作用[48]。另外,多糖对乳液的稳定效果受盐离子强度和pH值的影响。ι-卡拉胶可以增强高盐离子大豆油体乳液的稳定性[47],黄原胶可以提高小麦蛋白基O/W乳化液在高盐离子强度时的稳定性,而果胶可以提高其在酸性条件下的稳定性,却不能抵抗离子强度的影响[49]。可能是盐离子强度较大时,破坏了多糖和蛋白乳滴之间的相互作用力,多糖即从蛋白表面解吸,导致液滴聚集和絮凝。蔗糖和ι-卡拉胶[48]或果胶[49-50]共同使用,还可以改善乳化液的冻融稳定性,原因可能是蔗糖可以增加体系粘度,限制了水的移动,降低了油滴被迫接近的程度,而多糖通过改变油体表面的化学性质增加了乳化体系的稳定性。
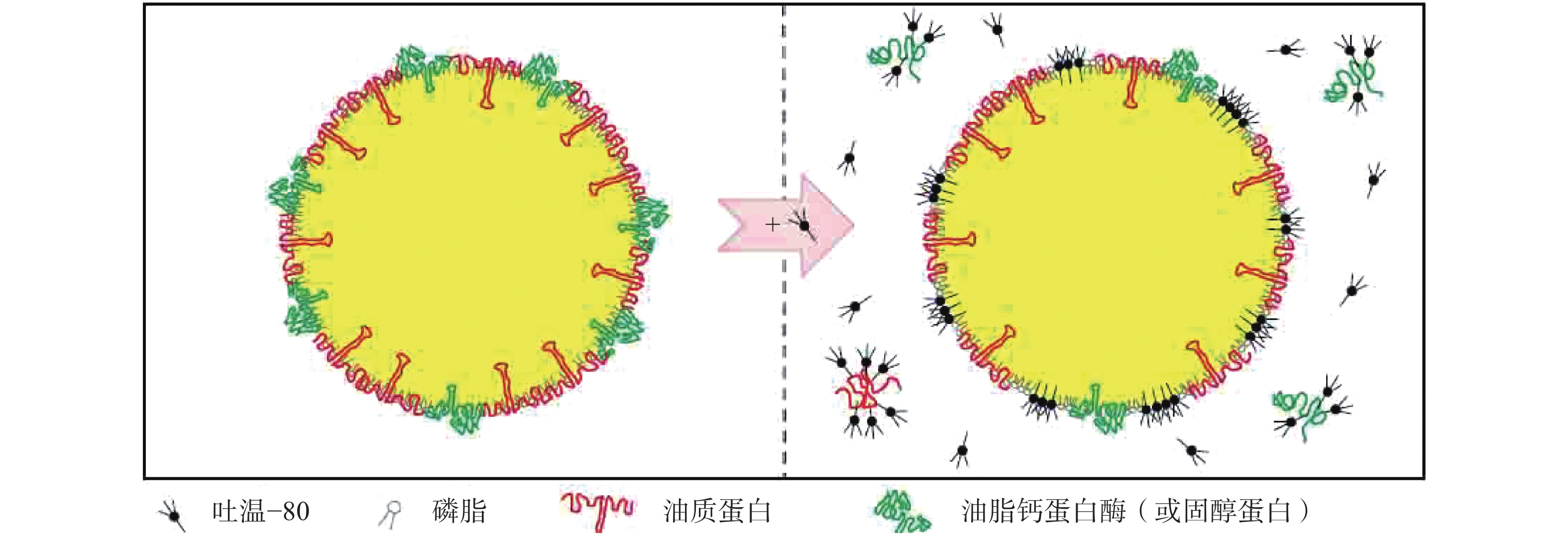
吐温−80是一种典型的非离子型表面活性剂,可竞争性置换油体表面的蛋白质(主要是油质钙蛋白和油质固醇蛋白),使得磷脂分子重排,形成更为紧密的表面活性剂-磷脂单分子层结构,相邻油体靠近时会形成一层薄的液体膜。一方面,由于部分油质蛋白被置换,油体表面的负电荷减少,静电斥力减小;另一方面,亲水性表面活性剂的嵌入使得油体表面亲水性增强,相邻油体之间的空间斥力增加。两种作用相互平衡,最终朝着有利于薄膜形成的方向发展,从而提高乳化液的稳定性[9,19],如图2示。
皂素是一种天然的小分子表面活性剂,由三萜类或甾类疏水性配基和寡糖链(亲水性)通过酯或醚键相连而成。可以在油水界面形成粘弹性的膜,在剪切变形中具有较高的絮凝稳定性[51]。皂树苷(68.21%皂素,1.6%蛋白,4.52%多酚)具有良好的表面活性,是一种常用的天然表面活性剂,可用于脂溶性分子的胶束化,从而提高脂溶性生物活性成分的水溶性[52]。有研究报道,多种植物皂素提取物,如甜菜提取物(0.50%皂素,4.00%蛋白,0.07% 多酚)、丝兰树提取物(9.50% 皂素,1.39% 蛋白, 22.44% 糖)具有与皂树苷相当的乳化稳定性[53-54]。在水法提取茶籽油过程中,茶皂素和多糖、蛋白质等一起参与形成乳化液[55]。摩洛哥坚果壳的皂素粗提物(23.53%皂素,7.44%蛋白,22.64%碳水化合物)[56]具有优良的乳化稳定性。虽然皂素提取物的皂素含量差别较大,但均具有良好的乳化稳定性,其机理可能是体相中的表面活性化合物的协同作用,蛋白质-皂素吸附至两相界面,增大液滴之间的静电斥力和空间位阻。由皂素粗提物稳定的乳液在pH5~8水溶液中大部分能保持稳定,但是热稳定性较差,可能是皂苷或皂苷-蛋白复合物的某些特定部分被降解导致两亲性的降低或消失,从而导致稳定性下降,也可能是其中的蛋白受热变性和皂苷聚合形成大分子复合物,导致稳定性下降[52-54,56]。
4. 总结及展望
植物油体表面特殊的磷脂-蛋白质单层膜维持了油体的结构稳定,可以抵抗干燥、高温等外界不利条件,在种子的成熟和萌发过程中发挥重要作用。植物油体富含中性脂,可以利用其与其他组分的比重和溶解性差异采用水法提取。在植物油体的水法提取过程中,溶液的pH、盐离子强度、去污剂等环境条件以及研磨方法、提取和洗涤次数等因素会影响油体的纯度和得率,因此,可根据需要通过控制提取和洗涤条件得到纯油体,提高油体的得率。关于油体乳化机理的研究较少。油体乳液中的乳化组分,如磷脂、蛋白质、多糖及外加表面活性剂通过改变油体表面电荷分布和蛋白质的空间构象,影响油体之间的相互作用力和空间位阻,改变油体乳液的粘度等从而影响油体乳液的稳定性。由于原料来源、提取和洗涤条件的差异,油体乳液乳化体系组成千差万别,乳化机理尚不清晰,因此应加大对不同油体乳液乳化体系的乳化机理研究,有望改进油体乳液的破乳效果,提高植物油水(酶)法的油脂得率,提高经济效益,同时对于天然预乳化油产品的开发和应用将产生巨大的推动效果,极大地拓宽植物油体的应用领域。
-
图 1 植物油体的结构模型[11]
注:油质蛋白分子相当于一个11 nm的柄状结构(中心疏水的发夹结构)附着在一个两亲性球状结构上(相当于未知二级结构的N-末端两亲性结构域和C-末端两亲性的α-螺旋结构域)。实线和圆表示亲水性组分,虚线表示疏水性组分。两线相连的黑色球体和三线相连的阴影球体分别代表磷脂和三酰甘油。(左)油体的尺寸与分子尺寸的比例被缩小了24倍;表面分子的曲率要比天然油体的曲率大得多(576倍);磷脂与油体的摩尔比保持与天然油体的摩尔比;油质蛋白与磷脂和油质蛋白的摩尔比显著降低。(中)垂直于表面的一个小的表面切片,显示两个油质蛋白分子和两个磷脂分子。(右)由13个磷脂分子和1个油质蛋白分子组成的结构单元的表面图。为了清晰地说明该结构单元,还展示了相邻的另外三个油质蛋白分子和四个磷脂分子。上面的图是在油质蛋白球体方向的视图,下面的图是在磷脂头部方向的视图。
Figure 1. Structural model of oil bodies[11]
油体来源 油菜籽 芥菜籽 棉籽 亚麻籽 玉米胚芽 花生 芝麻 车前草籽 脂质含量(%) 94.21 94.64 96.99 97.65 97.58 98.17 97.37 96.80 蛋白含量(%) 3.46 3.25 1.70 1.34 1.43 0.94 0.59 0.90 磷脂组成(%) 1.97 1.60 1.18 0.90 0.91 0.80 0.57 − 磷脂酰胆碱 59.50 53.10 58.60 57.20 64.10 61.60 41.20 55.10 磷脂酰丝氨酸 20.20 18.30 18.70 33.10 20.20 25.00 22.10 31.20 磷脂酰肌醇 14.00 13.10 18.10 6.90 7.60 8.40 20.90 11.70 磷脂酰乙醇胺 5.90 15.50 4.60 2.80 8.10 5.00 15.80 4.00 注:“−”表示文献中未列出。 -
[1] Laibach N, Post J, Twyman R M, et al. The characteristics and potential applications of structural lipid droplet proteins in plants[J]. Journal of Biotechnology,2015,201:15−27. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.08.020
[2] 杨建远, 陈芳, 宋沥文, 等. 油茶籽油提取技术研究进展[J]. 食品与机械,2016,32(2):183−187. [3] 梁帆, 郭华, 周玥. 4种工艺制取的油茶籽油的品质分析及比较[J]. 食品科技,2016,41(5):196−200. [4] Zaaboul F. 花生油体的分离、理化特性研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2018: 50−61. [5] 杨辉. 茶油提取新工艺及其品质的研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2012: 70-71. [6] Gai Q Y, Jiao J, Wei F Y, et al. Enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction of oil from Forsythia suspense seed and its physicochemical property and antioxidant activity[J]. Industrial Crops & Products,2013,51:274−278.
[7] Tzen J T C, Cao Y Z, Laurent P, et al. Lipids, proteins, and structure of seed oil bodies from diverse species[J]. Plant Physiology,1993,101(1):267−276. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.1.267
[8] Payne G, Lad M, Foster T, et al. Composition and properties of the surface of oil bodies recovered from echium plantagineum[J]. Colloids and Surfaces Bio-interfaces,2014,116:88−92. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.11.043
[9] Nikiforidis C V, Matsakidou A, Kiosseoglou V. Composition, properties and potential food applications of natural emulsions and cream materials based on oil-bodies[J]. RSC Advances,2014,4:25067−25078. doi: 10.1039/C4RA00903G
[10] 赵路苹. 大豆油体富集物的蛋白质组成及其对油体乳液性质的影响研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2017. [11] Tzen J T, Huang A H C. Surface structure and properties of plant seed oil bodies[J]. Journal of Cell Biology,1992,117 (2):327−335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.327
[12] Huang, Yu C. Evolution and functions of oleosins and oleosin-coated oil bodies in plants[D]. California: University of California, 2013: 98−130.
[13] Chen J C F, Tzen J T C. An in vitro system to examine the effective phospholipids and structural domain for protein targeting to seed oil bodies[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology,2001,42(11):1245−1252. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pce160
[14] Chen J C F, Tsai C C Y, Tzen J T C. Cloning and secondary structure analysis of caleosin, a unique calcium-binding protein in oil bodies of plant seeds[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology,1999,40(10):1079−1086. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a029490
[15] Lin L J, Sorgan S K T, Peng C C, et al. Steroleosin, a sterol-binding dehydrogenase in seed oil bodies[J]. Plant Physiology,2002,128 (4):1200−1211.
[16] Nikiforidis C V, Karkani O A, Kiosseoglou V. Exploitation of maize germ for the preparation of a stable oil-body nano-emulsion using a combined aqueous extraction-ultrafiltration method[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(5):1122−1127. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.10.009
[17] Nikiforidis C V, Kiosseoglou V. Aqueous extraction of oil bodies from maize germ (Zea mays) and characterization of the resulting natural oil-in-water emulsion[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2009,57(12):5591−5596. doi: 10.1021/jf900771v
[18] Nikiforidis C V, Kiosseoglou V. Physicochemical stability of maize germ oil body emulsions as influenced by oil body surface-xanthan gum interactions[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2010,58(1):527−532. doi: 10.1021/jf902544j
[19] Nikiforidis C V, Kiosseoglou V. Competitive displacement of oil body surface proteins by Tween 80-Effect on physical stability[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25 (5):1063−1068. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.10.002
[20] Nikiforidis C V, Donsouzi S, Kiosseoglou V. The interplay between diverse oil body extracts and exogenous biopolymers or surfactants[J]. Food research international,2016,83(5):14−24.
[21] Simona, Bettini, Angelo, et al. Reconstituted oil bodies characterization at the air/water and at the air/oil/water interfaces[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2014,122:12−18. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.06.044
[22] Tzen J T C, Peng C C, Cheng D J, et al. A new method for seed oil body purification and examination of oil body integrity following germination[J]. Journal of Biochemistry,1997,121(4):762−768. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021651
[23] Jolivet P, Boulard C, Bellamy A, et al. Protein composition of oil bodies from mature Brassica napus seeds[J]. Protomics,2009,9(12):3268−3284. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200800449
[24] 仇键. 油茶种子油体蛋白基因的分离克隆及其原核表达[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2006. [25] Hou J, Feng X, Jiang M, et al. Effect of NaCl on oxidative stability and protein properties of oil bodies from different oil crops[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2019,113:1−9.
[26] Chen Y, Ono T. Simple extraction method of non-allergenic intact soybean oil bodies that are thermally stable in an aqueous medium[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2010,58(12):7402−7407. doi: 10.1021/jf1006159
[27] Chen B, Mcclements D J, Gray D A, et al. Physical and oxidative stability of pre-emulsified oil bodies extracted from soybeans[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,132(3):1514−1520. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.11.144
[28] Zaaboul F, Raza H, Chen C, et al. Characterization of peanut oil bodies integral proteins, lipids, and their associated phytochemicals[J]. Journal of Food science,2018,83(1-3):93−100.
[29] Kapchie V N, Towa L T, Hauck C, et al. Evaluation of enzyme efficiency for soy oleosome isolation and ultrastructural aspects[J]. Food Research International,2010,43(1):241−247. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2009.09.019
[30] Chirico S D, Bari V D, Foster T, et al. Enhancing the recovery of oilseed rape seed oil bodies (oleosomes) using bicarbonate-based soaking and grinding media[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,241:419−426. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.008
[31] Chirico S D, Bari V D, María Juliana Romero Guzmán, et al. Assessment of rapeseed oil body (oleosome) lipolytic activity as an effective predictor of emulsion purity and stability[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,316:126355. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126355
[32] Pimentel, Lígia, Fontes A L, et al. Suitable simple and fast methods for selective isolation of phospholipids as a tool for their analysis[J]. Electrophoresis,2018,39(15):1835−1845. doi: 10.1002/elps.201700425
[33] Avalli A, Contarini G. Determination of phospholipids in dairy products by SPE/HPLC/ELSD[J]. Journal of chromatography,2005,1071(1−2):185−190. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2005.01.072
[34] Bourgeois C, Gomaa A I, Lefèvre T, et al. Interaction of oil bodies proteins with phospholipid bilayers: A molecular level elucidation as revealed by infrared spectroscopy[J]. Biomac, 2018, 122: 873−881.
[35] Eibl H. Phospholipids as functional constituents of biomembranes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2010,23(4):257−271.
[36] Zhou L Z, Chen F S, Li H H, et al. Peanut oil body composition and stability[J]. Journal of Food Science,2019,84(4):2812−2819.
[37] Li Y, Liu B, Jiang L. Interaction of soybean protein isolate and phosphatidylcholine in nanoemulsions: A fluorescence analysis[J], Food Hydrocolloids, 2018, 87: 814−829.
[38] Zhang Y, Yang N, Xu Y, et al. Improving the stability of oil body emulsions from diverse plant seeds using sodium alginate[J]. Molecules,2019,24(21):3856−3867. doi: 10.3390/molecules24213856
[39] Chang C, Tu S, Ghosh S, et al. Effect of pH on the inter-relationships between the physicochemical, interfacial and emulsifying properties for pea, soy, lentil and canola protein isolates[J]. Food Research International,2015,77(3):360−367.
[40] Yan Z, Zhao L, Kong X. Behaviors of particle size and bound proteins of oil bodies in soymilk processing[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,194:881−890. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.100
[41] Zhao L, Chen Y, Chen Y, et al. Effects of pH on protein components of extracted oil bodies from diverse plant seeds and endogenous protease-induced oleosin hydrolysis[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,200(6):125−133.
[42] Qi B, Ding J, Wang Z, et al. Deciphering the characteristics of soybean oleosome-associated protein in maintaining the stability of oleosomes as affected by pH[J]. Food research international,2017,100(1):551−557.
[43] Juliana M R G, Petris V, Chirico S D, et al. The effect of monovalent (Na+, K+) and divalent (Ca2+, Mg2+) cations on rapeseed oleosome (oil body) extraction and stability at pH 7[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,306:1−6.
[44] Gurtovenko A A, Vattulainen I. Effect of NaCl and KCl on phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine lipid membranes: Insight from atomic-scale simulations for understanding salt-induced effects in the plasma membrane[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2008,112(7):1953−1962. doi: 10.1021/jp0750708
[45] Allouche D, Parello J, Sanejouand Y H. Ca2+/Mg2+ exchange in parvalbumin and other EF-hand proteins: A theoretical study[J]. Journal of molecular biology,1999,285(2):857−873. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2329
[46] Guzey D, Mcclements D J. Impact of electrostatic interactions on formation and stability of emulsions containing oil droplets coated by β-Lactoglobulin and pectin complexes[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2007,55(2):475−485. doi: 10.1021/jf062342f
[47] Wu N N, Huang X, Yang X Q, et al. Stabilization of soybean oil body emulsions using ι-carrageenan: Effects of salt, thermal treatment and freeze-thaw cycling[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2012,28(1):110−120. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.12.005
[48] Wu N N, Yang X Q, Teng Z, et al. Stabilization of soybean oil body emulsions using κ, ι, λ-carrageenan at different pH values[J]. Food Research International,2011,44(4):1059−1068. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.03.019
[49] Qiu C, Zhao M, McClements D J. Improving the stability of wheat protein stabilized emulsions: Effect of pectin and xanthan gum addition[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,43:377−387. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.06.013
[50] Iwanaga D, Gray D, Decker E A, et al. Stabilization of soybean oil bodies using protective pectin coatings formed by electrostatic deposition[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2008,56(6):2240−2245.
[51] Tsibranska S, Tcholakova S, Golemanov K, et al. Role of interfacial elasticity for the rheological properties of saponin-stabilized emulsions[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2019.
[52] Tippel J, Lehmann M, Von Klitzing R, et al. Interfacial properties of quillaja saponins and its use for micellisation of lutein esters[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,212(10):35−42.
[53] Ralla T, Salminen H, Edelmann M, et al. Stability of emulsions using a new natural emulsifier: Sugar beet extract (Beta vulgaris L.)[J]. Food Biophysics,2017,12(3):269−278. doi: 10.1007/s11483-017-9482-7
[54] Ralla T, Salminen H, Tuosto J, et al. Formation and stability of emulsions stabilised by Yucca saponin extract[J]. International Journal of Food science and Technology,2018,53:1−8. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.13702
[55] 杨建远. 水法提取茶油过程中天然组分乳化机制及破乳提油技术的研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2019. [56] Bouhoute M, Taarji N, Vodo S, et al. Formation and stability of emulsions using crude extracts as natural emulsifiers from argan shells[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2020.
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 王雷,闵文杰,边帅杰,刘禹希,刘莉,齐滨. 基于指纹图谱和多成分测定研究不同类型黄酒对酒黄芩饮片质量的影响. 中草药. 2025(01): 79-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 代桂丽,张超锋. 反相高效液相色谱-脉冲安培检测法对硫酸新霉素的药物分析研究. 化学与粘合. 2024(02): 200-205 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 林立,孙海波,邱云,刘莉,齐云肖,杨彦丽,曹瑀. 基于滴定法与色谱法测定糖的干扰因素分析. 环境化学. 2024(07): 2512-2516 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 江竹莲,陈雪煜,王林. 离子色谱与三重四极杆质谱TSQ Altis联用实现10种寡糖的同时分析检测. 环境化学. 2022(04): 1453-1456 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 毛晴岚. 离子色谱法检测蜂蜜中的淀粉糖浆. 现代食品. 2022(09): 166-169 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 徐娟,付晓娜,周海,刘祥义. 黄精多糖提取、单糖组成及抗氧化活性分析. 粮食与油脂. 2022(07): 141-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 戴晨颖,洪诚毅,阙茂垚,梁瑞芳,张晓婷,范群艳,柳训才. 离子色谱在食品分析中的应用进展. 食品工业科技. 2022(19): 453-461 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 张亚军,李菲,梁廷银. 酵母培养物中甘露聚糖与β-葡聚糖含量的测定方法研究. 饲料研究. 2022(23): 118-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



